Abstract
INTRODUCTION
Ibrutinib is a Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor used for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), with a high rate of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) and associated treatment discontinuation.
Ibrutinib is mainly metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) CYP3A. The functionality of the enzyme is mainly influenced by gender and induction and inhibition by multiple substances. Therefore, it is necessary to know the pharmacokinetic profile of ibrutinib when it interacts with the CYP enzyme system, which can affect the metabolism and elimination of the drug, as well as alter its safety and efficacy profile. On the other hand, there is some controversy as to whether it is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), encoded by ABCB1, since there are studies that confirm this and others that deny it. If ibrutinib is a substrate of P-gp, this transporter could decrease its concentration and, therefore, its therapeutic efficacy.
The most common ADRs associated with ibrutinib are diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, bleeding, fatigue and cardiac-related ADRs. Toxicity to ibrutinib has been described as the most common reason for discontinuation.
OBJECTIVE
The aim of this project is to evaluate the influence of polymorphisms in metabolizing enzymes and transporters on the toxicity of ibrutinib.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This is a post-authorization, observational, retrospective and/or prospective follow-up study in a cohort of CLL patients treated with ibrutinib. All variables were collected from the patients' medical records.
Seven polymorphisms in CYP3A, ABCB1, ABCG2 and SLC01B1 were analyzed by qPCR using TaqMan® allelic discrimination assays on a ViiA7 (Thermofisher).
To assess safety, the incidence of adverse events was collected and their causality was determined using the algorithm of the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System.
RESULTS
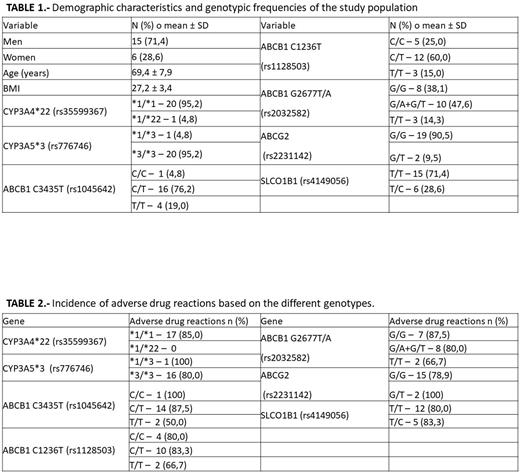
A total of 21 patients were included. The main demographic characteristics are shown in Table 1.
71.4% of the patients were men and 28.6% were women with a mean age of 68.3 ± 7.5 and 72.3 ± 8.8 (p=0.298), respectively. The value on the Charlson Comorbidity index was ≥ 5 in 67% of the patients. The main comorbidities were diabetes (n=3, 14%), mild liver pathology (n=3, 14%), chronic lung disease (n=2, 9.5%), congestive heart failure (n=1, 4.7%), connective tissue pathology (n=1, 4.7%), renal pathology (moderate or severe) (n=1, 4.7%) and neoplasms (n=1, 4.7%). The mean survival rate at 10 years was 27.4%.
A total of 83 adverse events were recorded, of which 45 (54%) were considered ADRs due to their causality determined as possible/probable/defined.
Eighty-one percent of the patients presented some type of toxicity, the most frequent being bleeding (33.3%), followed by musculoskeletal (19%), blood and lymphatic system (14.3%) and nervous system disorders (14.3%). The rate of treatment discontinuation due to toxicity was 20%.
The genotypic frequencies of the polymorphisms analyzed are described in Table 1. No significant association was found between polymorphisms in ABCB1, ABCG2, SLCO1B1, CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 and the incidence of ADRs (Table 2), probably due to the small sample size. A slight trend can be observed in subjects with mutated genotype of ABCB1 C3435T, C1236T and G2677T/A polymorphisms.
CONCLUSIONS
CLL treatment has a high rate of ADR, the main risk being bleeding. So far, polymorphisms in enzymes and transporters involved in the ibrutinib pathway have not been shown to affect the incidence of ADR in CLL patients, probably due to the small sample size of our study.
In addition to increasing the sample size, steady-state plasma concentrations of ibrutinib will be measured in order to correlate drug levels with polymorphisms in the genes analyzed and the incidence of ADR.
Disclosures
Loscertales:Roche: Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Lilly: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Speakers Bureau; Beigene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.